Table of Contents
Introduction
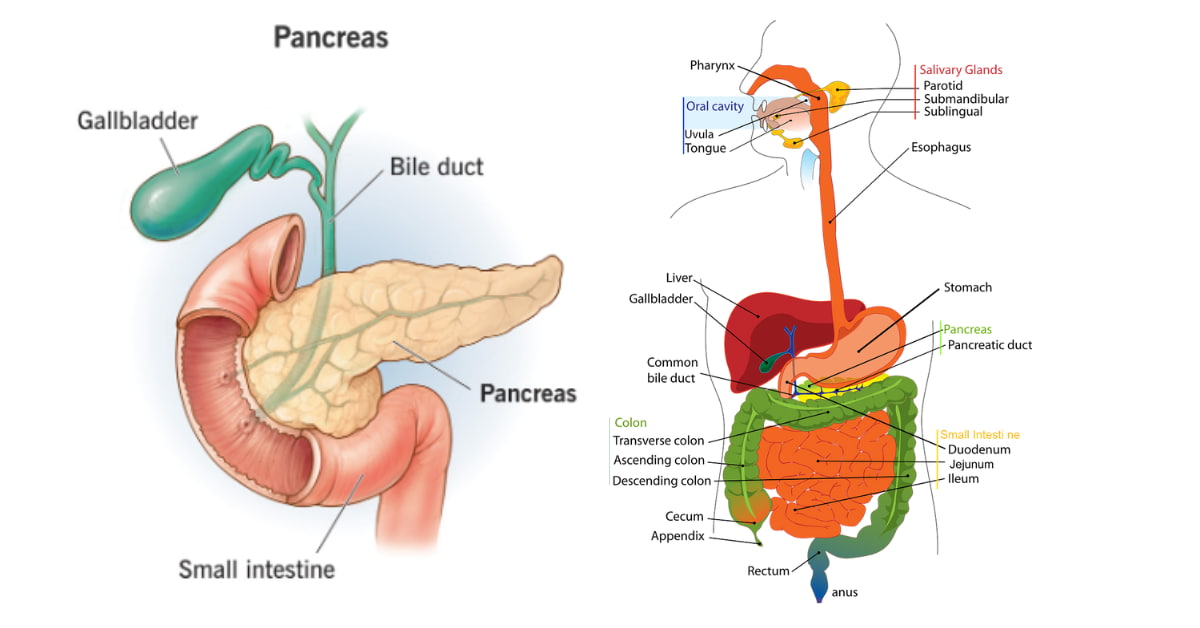
The Pancreas is part of the digestive system. It has 2 main functions: It makes enzymes that assist in breaking down food for digestion and hormones that assist in maintaining blood sugar levels and storing energy from food. It has two kinds of cells, each producing a different substance.
- Endocrine cells: It produce insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide hormones. Insulin assists lower blood sugar, and glucagon raises blood sugar.
- Exocrine cells: They produce enzymes that assist in digesting food in the intestine. chymotrypsin and Trypsin break down proteins. Amylase digests carb, and lipase breaks down fats.
Pancreas
It is a gland that makes hormones, including insulin, that humans need to survive. Decades ago, severe problems with the it were almost always mortal. Now, it is possible for people to live without a it.
Surgery to detach or remove it is known as pancreatectomy. The surgery may be partial, removing only the ill portion of it, or a surgeon may detach the entire Pancreas.
An absolute pancreatectomy that detaches the entire Pancreas also requires the removal or detachment of parts of the stomach, a part of the small intestine known as the duodenum, and the end of the bile duct. The gallbladder and spleen may also be removed.
This extensive surgery may be harmful and life-changing. After a pancreatectomy, an individual will develop diabetes. They need to modulate their lifestyle and diet and will have to take insulin for a whole lifetime.
A person who cannot make enough insulin develops diabetes, so removing it automatically activates the condition.
Removing it may also reduce the body’s ability or capacity to absorb nutrients from food. Without unnatural insulin injections and digestive enzymes, a person without a pancreas cannot survive.

Three primary types of hormones.
- Insulin: Produced by beta cells, insulin helps your body use blood sugar (glucose) as fuel for energy. Too much insulin causes low blood sugar, while insufficient insulin results in high blood sugar.
- Glucagon: Produced by alpha cells, glucagon helps balance out insulin by producing glucose to prevent hypoglycemia.
- Gastrin: Gastrin is a hormone that informs the stomach to make gastric acid. It has only creates a small amount of gastrin, and the stomach is the primary producer.
- Amylin: Located in beta cells, amylin inhibits food intake and delays stomach emptying.
- Somatostatin: Produced by delta cells, somatostatin regulates the endocrine system by inhibiting insulin and glucagon release.
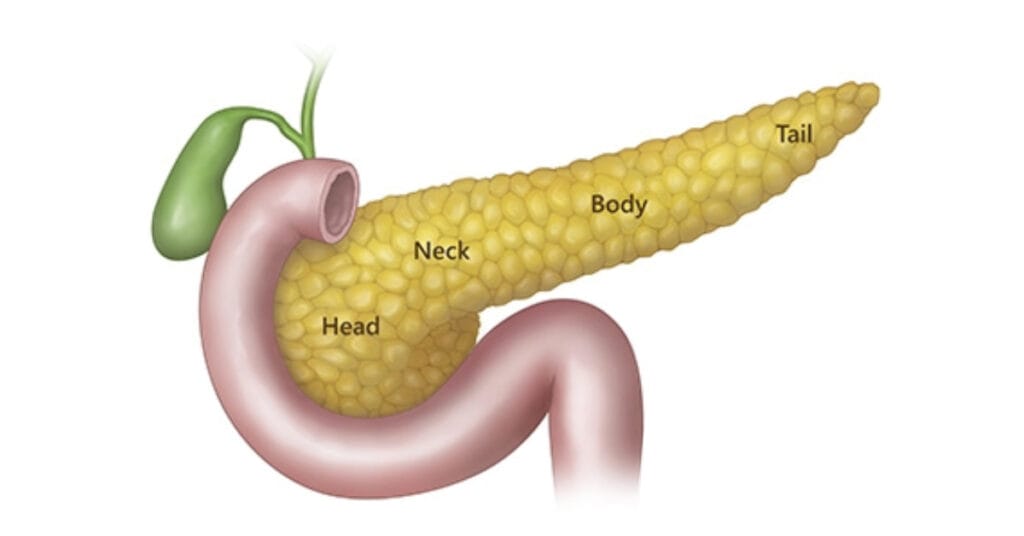
Anatomy
Parts are include the following:
- Head: The broader part of it sits in the curve of your duodenum.
- Neck: The short part extends from the head.
- Body: The middle of it between the head and neck extends upward.
- Tail: The thinnest part of it, located near your spleen.
Can we live without the Pancreas?
Yes, of course, you can, but not without side effects. Without the enzymes and hormones the Pancreas once produced, you’ll have difficulties regulating blood sugar and absorbing nutrients from food. You’ll need supplemental therapies to replace them.
In most cases, medical treatments can replace the Pancreas, but people without one require diligent observation and medical care. Removing it also means a person must make various lifestyle changes that can be tough to adjust to.
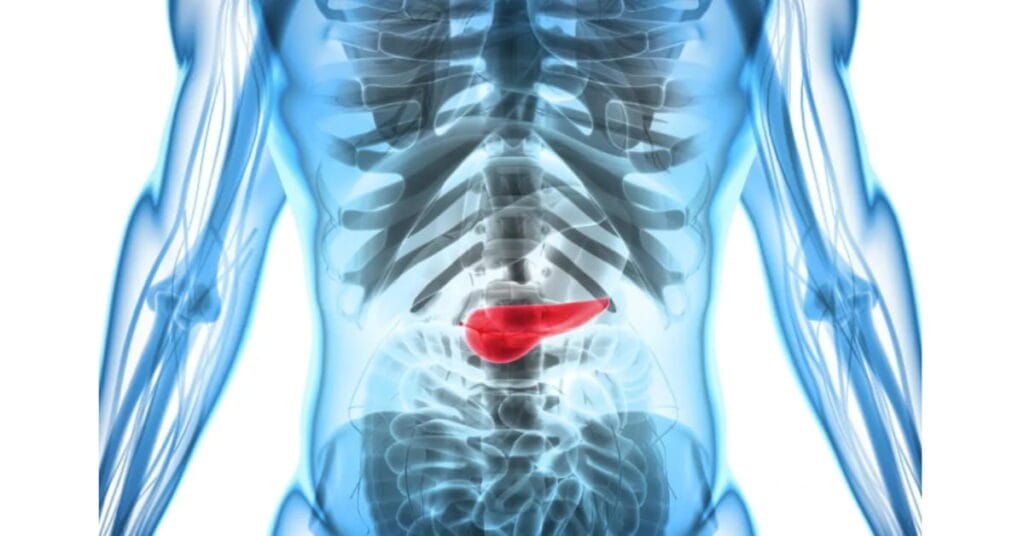
Function and Location
It is a flat, leaf-shaped gland located deep in the abdomen between the stomach & spine. Glands are organs that produce chemicals the body needs to function.
It is divided into 3 parts:
- A comprehensive end, known as the head.
- A thin end, known as the tail.
- A middle portion is understood as the body.
It constructs insulin, a hormone that controls blood sugar. When the body does not secrete insulin, blood sugar levels (blood glucose) may become critically high.
Without insulin to support the body’s absorption of blood glucose, the body is unable to use glucose from food. It may result in malnutrition and other serious health problems.
It also produces digestive juices that assist the body in breaking down and absorbing food. The part of it that makes digestive juices is the exocrine Pancreas, and the part responsible for secreting insulin is called the endocrine Pancreas.
Hormones come in the bloodstream, while digestive enzymes flow through a pancreatic duct tube into a portion of the small intestine called the duodenum. The gallbladder and liver also release digestive juices and other chemicals or compounds into the duodenum, allowing these organs to collaborate to help the body absorb food.
7 symptoms of pancreas problems
1. Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain is still a common sign & symptom of pancreatic disorders. It usually manifests as a painful & piercing sensation that moves from the top to the bottom of the abdomen. This type of pain may be chronic, or it goes backwards. Although individuals will have varied locations or positions or intensities of pain, it usually occurs just beneath the lower portion of the ribs in the region of the stomach’s or tummy’s upper cavity. Also, note that there could be some reasons for abdominal pain; hence, supplementary clinical symptoms & procedures are necessary for identifying pancreatic impingement.
2. Digestive Issues
Many people who suffer from pancreas problems experience digestion problems. The Pancreas is very important in digestion because it makes digestive enzymes that break food into small particles. When it gets affected, these enzymes can not get released appropriately, causing digestion problems. Some digestive issues include diarella, bloating, or excess gases, & impaired absorption of nutrients. For example, the malabsorption of fats may lead to fatty & stinky stools (steaturrhea). It gives rise to a state or condition of reduced appetite, which makes or create an individual lose weight as their bodies maynot digest crucial nutrients consumed from the food.
3. Unexplained Weight Loss
Unexpected or uncharacteristic weight loss may be considered one of the symptoms or signs of many pancreas issues, including some kinds of cancer. It is common for individuals to lose weight despite taking regularly, if not more than often.. This condition is caused by the body’s failure to absorb nutrients, which is caused by impaired work of the Pancreas. Malabsorption of nutrients such as fats may reduce body weight and general health status. Unexplained weight loss indicates severe hidden disease; therefore, a healthcare professional should constantly evaluate it.
4. Jaundice
Jaundice is a condition in which the skin and mucosa turn yellowish. It happens when bilirubin is made up in the blood. Yellow pigment, called as bilirubin, is produced from haemoglobin degradation in red blood cells. Bilirubin may not be efficiently dealt with or eradicated if the Pancreas and the bile ducts are involved. As a consequence, this leads to the buildup of bilirubin, which causes the skin & eyes to yellow. Yellowing is also accompanied by dark urine & pale stools caused by bilirubin buildup.
5. Changes In Stool Color
A change in colour in a stool may suggest a issue with the Pancreas, especially the bile ducts. When in good condition, faeces should be primarily brown because of the liver’s degradation and metabolism of bilirubin. It is, however, only sometimes the case. At times, when one contact with an obstruction in the normal or usual flow of bile as it moves from the liver to the intestines, the stools may be either whitish or clay coloured. Lack of bilirubin causes this alteration in colour, as it is what gives stool its standard brown colour. The amount of discolouration varies depending on the level of the obstructed bile flow.
6. Blood Sugar Fluctuations
The Pancreas presumes an important function by controlling blood glucose concentration using secreted insulin. As such, pancreatic disorders may cause significant disturbances in glycemic regulation. Two main scenarios can arise:
Insufficient insulin production is the failure of the Pancreas to make enough insulin in situations such as diabetes, specifically type 1 diabetes. As results, there is excess glucose in their blood, moving to high sugar blood levels and manifestations such as too much thirst, frequent urinating, extreme tiredness, and unusual weight reduction.
Overproduction of insulin: Pancreas problems can also cause too much insulin to be produced, leading to hypoglycemia. These conditions include dizziness, sweating, shaking, confusion, and, worse still, loss of consciousness.
7. Nausea And Vomiting
Persistent nausea & vomiting may also affect people who suffer from issues associated with the Pancreas. These symptoms could lead to severe dehydration & might exacerbate weight loss. They usually have nausea because of digestive disturbances or abdominal pain, as usual. Due to enzyme buildup in the Pancreas, the organ may become inflamed, resulting in vomiting as a result of the regurgitation of the stomach contents. Proper nutrition & hydration are critical for people experiencing nausea and vomiting. listade.
What are the various diseases of the Pancreas?
The common diseases of the Pancreas include pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer.
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the Pancreas. The Pancreas’s enzymes can digest part of the Pancreas and the surrounding fatty omentum in the abdomen. It most commonly originates from alcohol and gallstones, but certain medications, genetic predispositions, or dietary habits can also cause it.
Pancreatic cancer is most frequently an adenocarcinoma from the enzyme-producing and ductal cells. Rarely can cancer arise from the endocrine cells and is called a neuroendocrine tumour. Smoking and alcohol are the two most ordinary risk factors for cancer in the Pancreas. Pancreatitis itself may also be a risk factor.
Diseases like cysts, precancerous, or conditions like IPMN can affect the Pancreas.
How to Keep Your Pancreas Healthy
The following healthy lifestyle modifications may prevent pancreatic disorders & other associated issues as well as improve the overall digestive health:
- To keep your diet fat-free, include plenty of whole grains, fruits, & vegetables, especially broccoli, cauliflower, or cabbage.
- Exercise for at least thirty minutes daily & maintain a healthy weight to avert diabetes & gallstones.
- Avoid extreme fat diets that promise quick weight loss. The liver will thank you for it.
- Drink in moderation. Excessive alcohol utilisation is a called risk factor for pancreatitis & pancreatic cancer.
- Do not smoke cigarettes or any other tobacco products. About 20-30 percentage of pancreatic cancer cases are linked to tobacco usage.
- Get the Pancreas checked regularly. As with any issues, catching pancreatic cancer in its early stages may assist prevent cancerous cells from increasing and spreading.
Conclusion
It is a gland that makes hormones, including insulin, that humans need to survive. Decades ago, severe problems with the it were almost always mortal. Now, it is possible for people to live without a pancreas.
Surgery to detach or remove the Pancreas is known as pancreatectomy. The surgery may be partial, removing only the ill portion of the Pancreas, or a surgeon may detach the entire Pancreas.
The common diseases of the Pancreas include pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer.
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the Pancreas. The Pancreas’s enzymes can digest part of the Pancreas and the surrounding fatty omentum in the abdomen. It most commonly originates from alcohol and gallstones, but certain medications, genetic predispositions, or dietary habits can also cause it.
Pancreatic cancer is most frequently an adenocarcinoma from the enzyme-producing and ductal cells.